The World Economic Forum recently released its Global Information Technology Report 2013, and in this post I would like to have a quick look at it.
It is a long document, so I will just try to take a few highlights to give an idea of the findings.
The report has a Network Readiness Index that aims to measure how prepared countries are to adopt and make the most of new technology. Factors such as investment in broadband and other telecommunications fields obviously enter, but so does the quality of the education system and regulatory powers.
Finland leads the world in embracing technology, followed by Singapore and Sweden. The UK is in 7th place, the USA in 9th and my present home Italy is well down at number 50.

The Nordic countries and the so-called Asian Tigers – Singapore, Taiwan (China), South Korea and Hong Kong SAR – dominate this year’s index thanks to their business-friendly approach, highly skilled populations and investments in infrastructure, among other strengths. Finland, which arguably has one of the best educational systems in the world, stands out as a digital innovation hub.
Southern Europe shows a massive lag in fact with the North, and this is a major problem.
The positioning is not only important for so called ‘techies’, but really important for the economy as a whole, and here in Italy (and in Southern Europe on the whole) we are in serious need of economic improvement.
Latin America, the Caribbean and sub-Saharan Africa also suffer from a serious lag despite infrastructure improvements, an expansion of coverage and a push into e-government. Weaknesses in the political and regulatory environment, the existence of large segments of the population with a low skills base and poor development of the innovation system are all factors hindering Latin America’s technological potential. In sub-Saharan Africa, costly access to technology, a low skills base and unfavourable business conditions are among the chief obstacles.
The report demonstrates that economic growth and technological readiness are tightly linked.
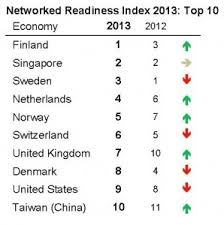
A look at the top 10
An analysis by Booz & Company has found that ICT could help lift millions out of poverty.
Digitization has boosted world economic output by US$ 193 billion over the past two years and created 6 million jobs during that period, according to the study. Using a Digitization Index that ranks countries on a scale from zero to 100, Booz & Company found that an increase of 10% in a country’s digitization score fuels a 0.75% growth in its GDP per capita. That same 10% boost in digitization leads to a 1.02% drop in a state’s unemployment rate.
If emerging markets could double the Digitization Index score for their poorest citizens over the next 10 years, the result would be a global US$ 4.4 trillion gain in nominal GDP, according to the study. It would generate an extra US$ 930 billion in the cumulative household income for the poorest, and 64 million new jobs for today’s socially and economically most marginal groups. This would enable 580 million people to climb above the poverty line.
So investment is this area is extremely important, but in many places falling profits due to economic downturn (as is the case in Southern Europe and to some extent the USA) mean that less money is available, and this effects future growth scenarios.
Interestingly 3G growth is more important than general mobile telecommunication growth, we really do live in an information society that is based on Internet connectivity.
Medical care is also another area where benefits are net and easy to measure.
Southern Europe is in a particularly precarious position due to lack of investment capability. Rwanda on the other hand is following many other African countries in investing in expanding its fibre optic network and hopes to become a banking and finance hub, moving to being a knowledge based economy and away from agrarian in the next 7 years.
Colombia, Uruguay and Panama have become champions of e-government and connectivity. In Colombia, Internet connections have tripled to 6.2 million in the last 2.5 years. In Uruguay, small and medium-sized tech enterprises helped lift technology exports from US$ 50 million in 2000 to US$ 225 million in 2010.
Here in Italy there is little investment and a distinct lack in centralized planning, so we will soon be slipping below these countries on the scale and continue to suffer the related threats on economic development that this situation provokes.
The report is free to download here. It is as I said long and detailed, but the rankings are in chapter 1 if you just want to see where your own country sits.



